What is Hydrogeology
Hydrogeology is the area of geology.
Download technical [.PDF]
Hydrogeology deals with the distribution and movement of groundwater in the soil and rocks of the Earth's crust.
MEANING OF HYDROGEOLOGY
Hydrogeology or groundwater hydrology deals with how water gets into the ground (recharge), how it flows in the subsurface (through aquifers) and how groundwater interacts with the surrounding soil and rock (the geology).
Hydrogeology or groundwater hydrology deals with how water gets into the ground (recharge), how it flows in the subsurface (through aquifers) and how groundwater interacts with the surrounding soil and rock (the geology).
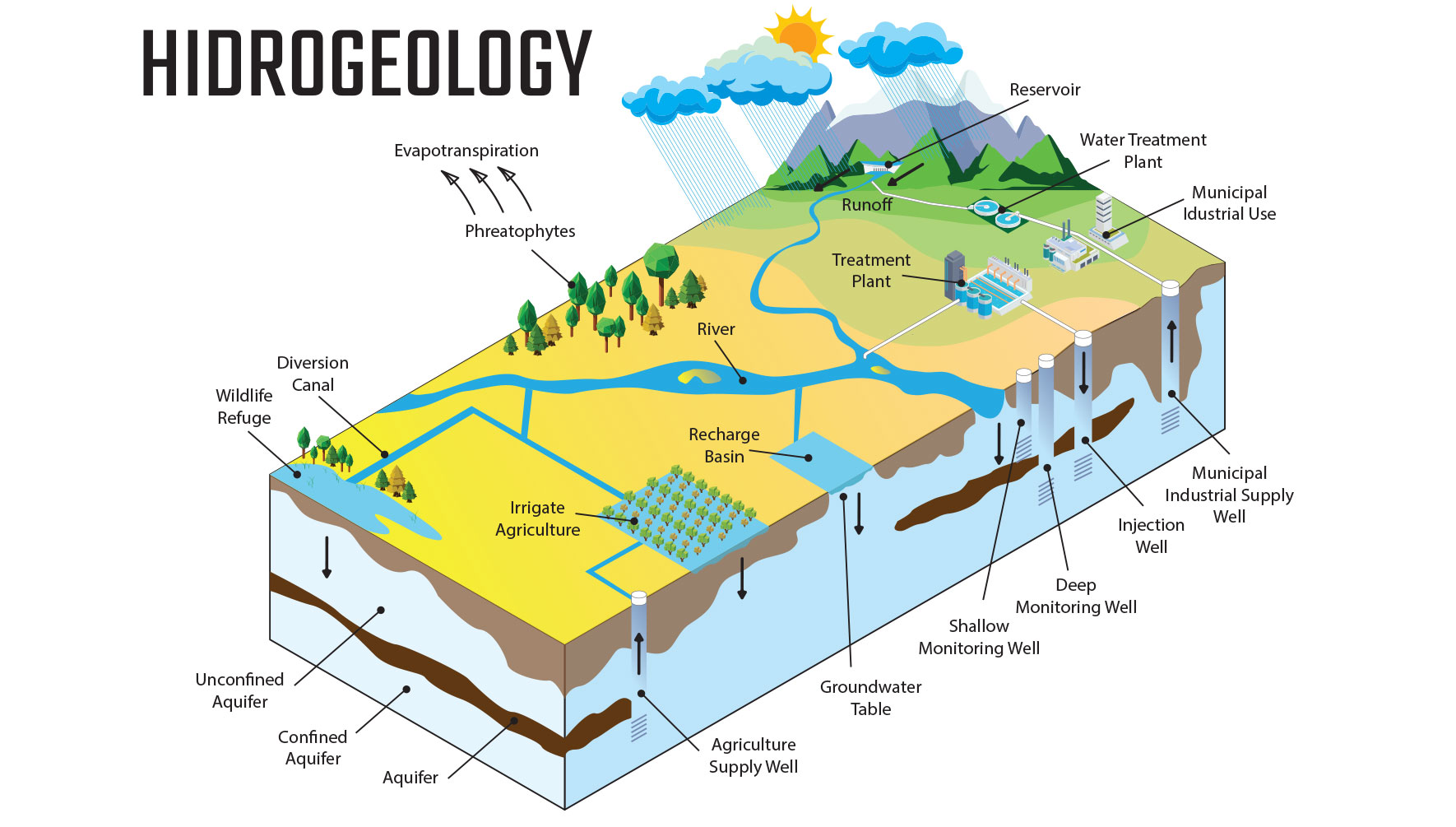
HYDROGEOLOGICAL RESEARCHES
A hydrogeological researches covers a multitude of topics such as the climatic conditions in the region, the rainfall regime, the chemical composition of water, the physical characteristics of the rock, such as permeability, porosity, fracturing, chemical composition, geological and geotectonic features.
In a hydrogeological study it is fundamental, apart from subsurface hydrology and geology, to have information related to:
Geophysical prospecting
techniques are used to determine the nature of the materials existing in the subsurface or in the surrounding area.
Hydrochemistry
the study of groundwater chemistry and groundwater quality to check if it complies with the regulations for groundwater use.
Drilling technology
in many studies the difference between success or failure is in the type of drilling and collection of the study material. For example, though a borehole.
WHAT DOES A HYDROGEOLOGIST DO?
Hydrogeologists work to solve some of the big challenges facing the world today, including sustainable water supply, food and energy production, as well as environmental protection and adapting to climate change. They may be involved in:
- Design and construction of water wells for drinking water, irrigation and other purposes;
- Study how much groundwater is available to sustain water supplies to prevent groundwater depletion and adverse impacts on natural baseflows to rivers and wetland ecosystems;
- Study water quality to ensure that it is fit for its intended use;
- Clean up of groundwater pollution;
- Construction dewatering schemes to help with groundwater problems associated with mining construction industry;
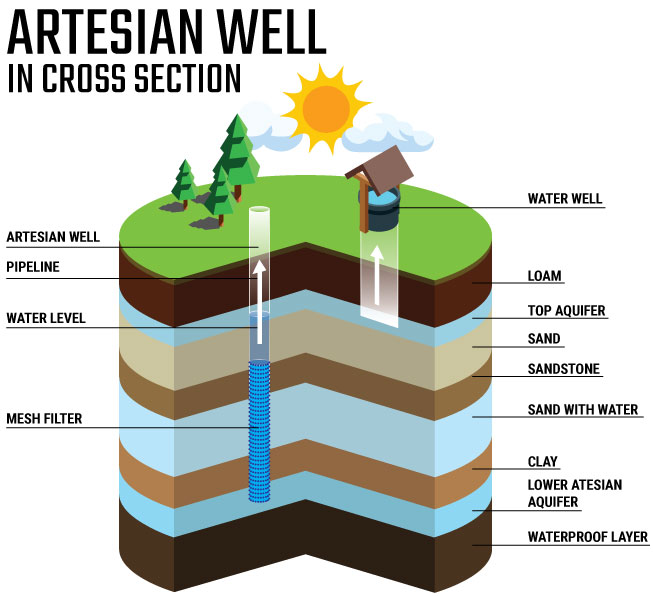
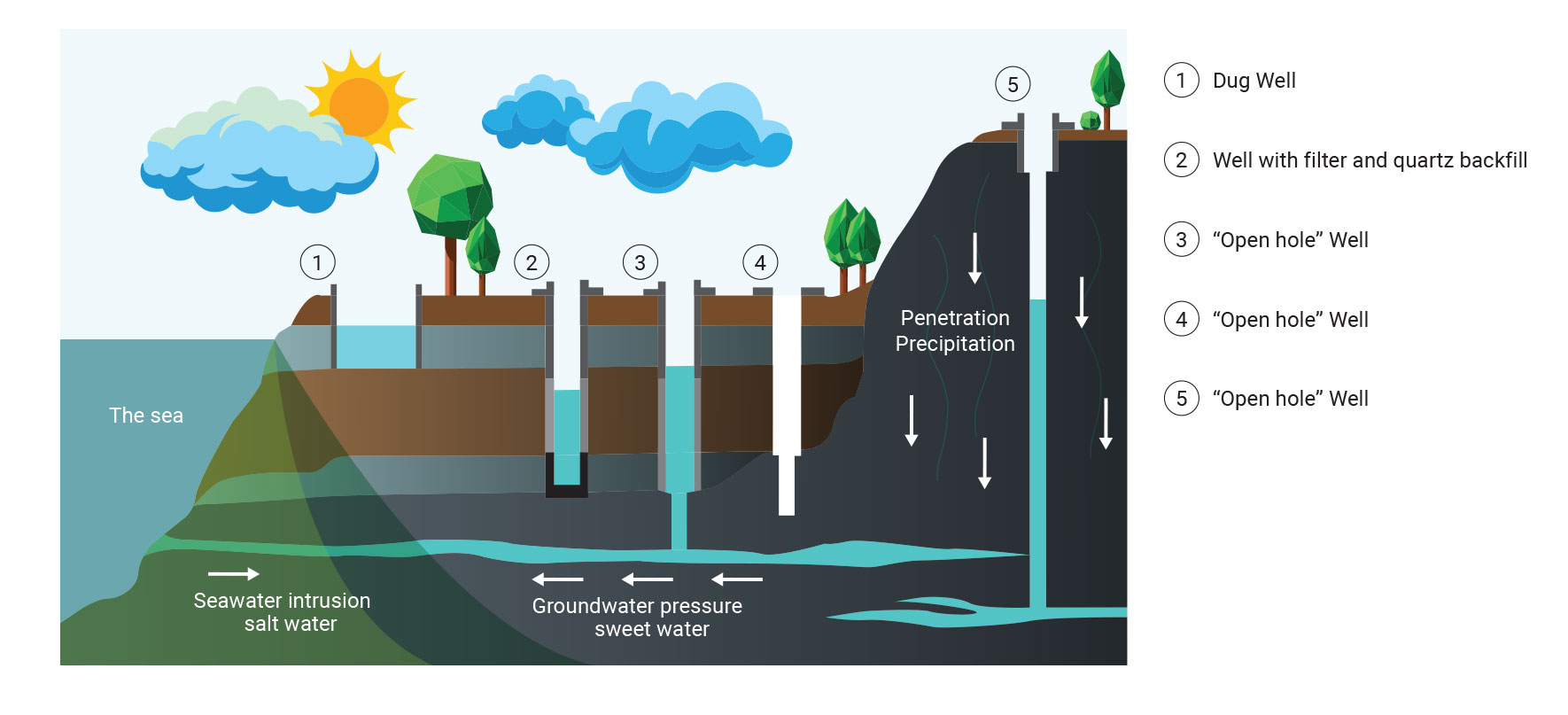
 QUINCE M PRO
QUINCE M PRO